计算机体系结构cs代写 I218代写 计算机体系结构作业代写
1510I218 Computer ArchitectureReport 3 计算机体系结构cs代写 (1) In the textbook and lecture slides, detailed information in the pipeline registers (IF/ID, ID/EX, EX/MEM, MEM/WB) is not provided. ...
View detailsSearch the whole station
公司财务原理代写 Chapter 1 Introduction to Corporate Finance 1) This book is mainly about: A) financial decisions made by corporations. B)
1) This book is mainly about:
A) financial decisions made by corporations.
B) financial decisions made by households.
C) financial decisions made by governments.
D) financial decisions made by employees.
2) Shareholders of a corporation may be, among others,
A) individuals.
B) individuals and pension funds.
C) pension funds.
D) individuals, pension funds, and insurance companies.
Generally, a corporation is owned by its
A) managers.
B) board of directors and shareholders.
C) shareholders.
D) managers, board of directors, and shareholders.
4) A corporation, potentially, has infinite life because it
A) is a legal entity.
B) has the same ownership and management.
C) has limited liability.
D) is closely regulated.
Limited liability is an important feature of:
A) sole proprietorships.
B) partnerships.
C) corporations.
D) both partnerships and corporations.
6) As a legal entity, a corporation can perform the following functions EXCEPT:
A) borrow money and lend money.
B) borrow money, lend money, and sue and be sued.
C) vote.
D) borrow money, lend money, sue and be sued, and vote.
Which of the following assets is tangible?
A) ExxonMobil’s corporate headquarters building
B) Apple Inc.’s trademark
C) Hewlett-Packard’s most recent printer patent
D) Microsoft’s technical expertise
8) Which of the following types of assets are intangible?
A) production machinery
B) factories
C) trademarks
D) office equipment
A firm’s investment decision is also called its
A) financing decision.
B) liquidity decision.
C) capital budgeting decision.
D) leasing decision.
10) Which of the following is not a financial asset?
A) common stock
B) bank loans
C) preferred stock
D) buildings
Which of the following is an important function of financial markets?
A) providing financing
B) providing financing and liquidity
C) providing financing, providing liquidity, reducing risk, and providing information
D) providing information
12) Disadvantages of the corporate form include:
A) agency costs
B) double taxation
C) cost of managing the corporation
D) all of the options
In the principal-agent framework:
A) shareholders are the principals.
B) managers are the principals.
C) managers are the agents.
D) shareholders are the principals and managers are the agents.
14) Costs associated with the conflicts of interest between the managers and the shareholders of a corporation are called:
A) legal costs.
B) bankruptcy costs.
C) administrative costs.
D) agency costs.
A corporation may incur agency costs because:
A) Managers may not attempt to maximize the value of the firm to shareholders.
B) Shareholders incur monitoring costs.
C) Of the separation of ownership and management.
D) All of the responses are correct.
16) The following groups are some of the claimants to a firm’s income stream:
A) shareholders and bondholders only.
B) shareholders, bondholders, and employees only.
C) shareholders, bondholders, employees, and management only.
D) shareholders, bondholders, employees, management, and government.
The financial goal of a corporation is to:
A) maximize profits.
B) maximize sales.
C) maximize the value of the firm for the shareholders.
D) maximize managers’ benefits.
18) The firm’s purchase of real assets is also referred to as the:
A) capital structure decision.
B) CFO decision.
C) financing decision.
D) capital investment decision.
The sale of financial assets by a corporation is also referred to as the
A) capital budgeting decision.
B) CFO decision.
C) financing decision.
D) investment decision.
20) The choice of the proper mixture of debt and equity, used to finance a corporation, is also referred to as the
A) capital budgeting decision.
B) capital structure decision.
C) investment decision.
D) liquidity decision.
Which of the following groups are referred to as stakeholders?
A) employees, customers, and suppliers only
B) shareholders only
C) employees and customers only
D) employees, customers, shareholders, and suppliers
22) The following are examples of real assets:
A) machinery, office buildings, and warehouses only.
B) machinery and office buildings only.
C) common stock only.
D) machinery only.
The following are examples of tangible assets except:
A) machinery only.
B) machinery and office buildings only.
C) training courses for employees only.
D) machinery, office buildings, and warehouses only.
24) The ultimate financial goal of a corporation is to:
A) minimize stockholder risk.
B) maximize profit.
C) maximize the value of the corporation to the stockholders.
D) increase size of the firm.
Mr. Free has $100 income this year and zero income next year. The market interest rate is 10 percent per year. If Mr. Free consumes $30 this year and invests the rest in the market, what will be his consumption next year?
A) $50
B) $55
C) $77
D) $100
26) Mr. Bird has $100 income this year and zero income next year. The market interest rate is 10 percent per year. Mr. Bird also has an investment opportunity in which he can invest $50 today and receive $80 next year. Suppose Mr. Bird consumes $30 this year and invests in the project. What will be his consumption next year?
A) $80
B) $82
C) $100
D) $102
Ms. Venus has $100 income this year and $110 next year. The market interest rate is 10 percent per year. Suppose Ms. Venus consumes $60 this year. What will be her consumption next year?
A) $120
B) $154
C) $170
D) $210
28) Mr. Thomas has $100 income this year and zero income next year. The market interest rate is 10 percent per year. Mr. Thomas also has an investment opportunity in which he can invest $50 this year and receive $80 next year. Suppose Mr. Thomas consumes $50 this year and invests in the project. What will be his consumption next year?
A) $50
B) $55
C) $80
D) $110
Mr. Dell has $100 income this year and zero income next year. The expected return from investing in the stock market is 10 percent a year. Mr. Dell also has an investment opportunity—having the same risk as the market in which he can invest $50 this year and receive $80 next year. Suppose Mr. Dell consumes $50 this year and invests in the project. What is the NPV of the investment opportunity?
A) $0
B) $5
C) $22.73
D) none of the options
30) Ms. Anderson has $60,000 income this year and $40,000 next year. The market interest rate is 10 percent per year. Suppose Ms. Anderson consumes $80,000 this year. What will be her consumption next year?
A) $18,000
B) $30,000
C) $60,000
D) $70,000
1) The present value of $100 expected two years from today at a discount rate of 6 percent is
A) $112.36.
B) $106.00.
C) $100.00.
D) $89.00.
2) Present value is defined as:
A) future cash flows discounted to the present by an appropriate discount rate.
B) inverse of future cash flows.
C) present cash flows compounded into the future.
D) future cash flows multiplied by the factor (1 + r)t.
If the annual interest rate is 12 percent, what is the two-year discount factor?
A) 0.7972
B) 0.8929
C) 1.2544
D) 0.8065
4) If the present value of cash flow X is $240, and the present value of cash flow Y is $160, then the present value of the combined cash flows is:
A) $240.
B) $160.
C) $80.
D) $400.
The rate of return is also called the:
A) discount rate.
B) discount rate and hurdle rate only.
C) discount rate, hurdle rate, and opportunity cost of capital.
D) discount rate and opportunity cost of capital only.
6) The present value of $121,000 expected one year from today at an interest rate (discount rate) of 10 percent per year is:
A) $121,000.
B) $100,000.
C) $110,000.
D) $108,900.
The one-year discount factor, at a discount rate of 25 percent per year, is:
A) 1.25.
B) 1.0.
C) 0.8.
D) 0.75.
8) The one-year discount factor, at an interest rate of 100 percent per year, is:
A) 1.50.
B) 0.50.
C) 0.25.
D) 1.00.
The present value of $100,000 expected at the end of one year, at a discount rate of 25 percent per year, is:
A) $80,000.
B) $125,000.
C) $100,000.
D) $75,000.
10) If the one-year discount factor is 0.8333, what is the discount rate (interest rate) per year?
A) 10 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 30 percent
D) 40 percent
If the present value of $480 to be paid at the end of one year is $400, what is the one-year discount factor?
A) 0.8333
B) 1.20
C) 0.20
D) 1.00
12) If the present value of $250 expected one year from today is $200, what is the one-year discount rate?
A) 10 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 30 percent
If the one-year discount factor is 0.90, what is the present value of $120 expected one year from today?
A) $100
B) $96
C) $108
D) $133
14) If the present value of $600, expected one year from today, is $400, what is the one-year discount rate?
A) 15 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
The present value formula for a cash flow expected one period from now is:
A) PV = C1 × (1 + r).
B) PV = C1/(1 + r).
C) PV = C1/r.
D) PV = (1 + r)/C1.
16) The net present value formula for one period is:
A) NPV = C0 + [C1/(1 + r)].
B) NPV = PV required investment.
C) NPV = C0/C1.
D) NPV = C1/C0.
An initial investment of $400,000 is expected to produce an end-of-year cash flow of $480,000. What is the NPV of the project at a discount rate of 20 percent?
A) $176,000
B) $80,000
C) $0 (zero)
D) $64,000
18) If the present value of a cash flow generated by an initial investment of $200,000 is $250,000, what is the NPV of the project?
A) $250,000
B) $50,000
C) $200,000
D) -$50,000
What is the present value of the following cash flows at a discount rate of 9 percent?
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| $100,000 | $150,000 | $200,000 |
A) $372,431.81
B) $450,000.00
C) $405,950.68
D) $412,844.04
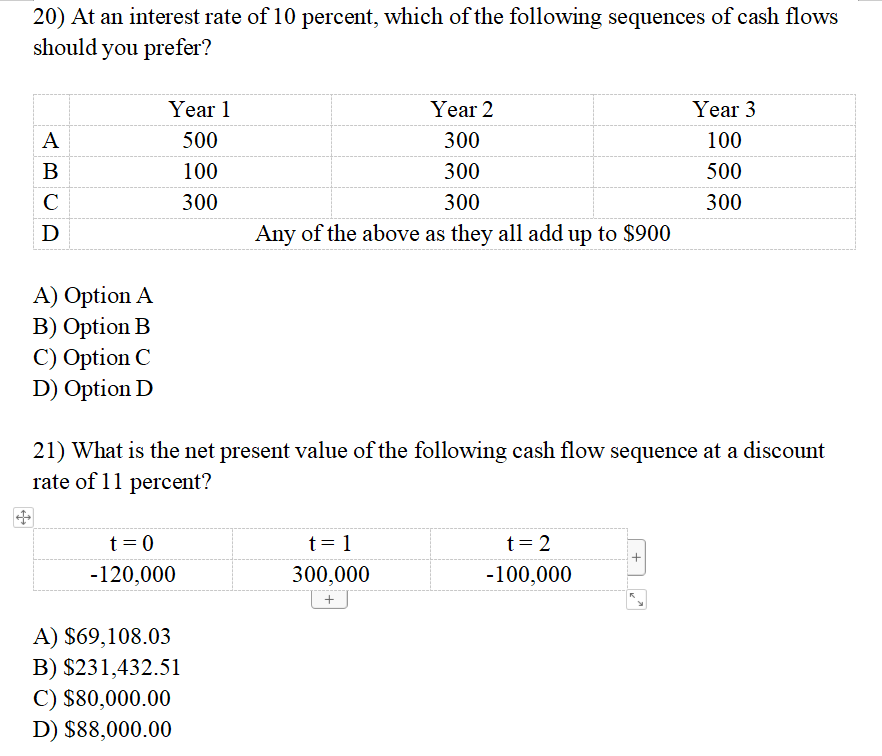
22) What is the net present value of the following sequence of annual cash flows at a discount rate of 16 percent APR?
| t = 1 | t = 2 |
| -100,000 | 300,000 |
A) $136,741.97
B) $122,948.87
C) $158,620.69
D) $139,418.23
What is the net present value (NPV) of the following sequence of cash flows at a discount rate of 9 percent?
| t = 0 | t = 1 | t = 2 | t = 3 | |
| -250,000 | 100,000 | 150,000 | 200,000 |
A) $122,431.81
B) $200,000.00
C) $155,950.68
D) $177,483.77
24) Which of the following statements regarding the NPV rule and the rate of return rule is false?
A) Accept a project if its NPV > 0.
B) Reject a project if the NPV < 0.
C) Accept a project if its rate of return > 0.
D) Accept a project if its rate of return > opportunity cost of capital.
An initial investment of $500 produces a cash flow of $550 one year from today. Calculate the rate of return on the project.
A) 10 percent
B) 15 percent
C) 20 percent
D) 25 percent
26) According to the net present value rule, an investment in a project should be made if the:
A) net present value is greater than the cost of investment.
B) net present value is greater than the present value of cash flows.
C) net present value is positive.
D) net present value is negative.
Which of the following statements regarding the net present value rule and the rate of return rule is false?
A) Accept a project if NPV > cost of investment.
B) Accept a project if NPV is positive.
C) Accept a project if return on investment exceeds the rate of return on an equivalent-risk investment in the financial market.
D) Reject a project if NPV is negative.
28) The opportunity cost of capital for a risky project is:
A) the expected rate of return on a government security having the same maturity as the project.
B) the expected rate of return on a well-diversified portfolio of common stocks.
C) the expected rate of return on a security of similar risk as the project.
D) the expected rate of return on a typical bond portfolio.
A perpetuity is defined as a sequence of:
A) equal cash flows occurring at equal intervals of time for a specific number of periods.
B) equal cash flows occurring at equal intervals of time forever.
C) unequal cash flows occurring at equal intervals of time forever.
D) unequal cash flows occurring at equal intervals of time for a specific number of periods.
30) Which of the following is generally considered an example of a perpetuity?
A) Interest payments on a 10-year bond
B) Interest payments on a 30-year bond
C) Interest payments on a consol
D) Interest payments on government bonds
1) The following entities issue bonds to engage in long-term borrowing EXCEPT:
A) the federal government.
B) state and local governments.
C) corporations.
D) individuals.
2) The type of bonds where the identities of bond owners are recorded and the coupon interest payments are sent automatically are called
A) bearer bonds.
B) government bonds.
C) registered bonds.
D) recorded bonds.
A government bond issued in France has a coupon rate of 5 percent, a face value of 100 euros, and matures in five years. The bond pays annual interest payments. Calculate the price of the bond (in euros) if the yield to maturity is 3.5 percent.
A) 100.00
B) 106.77
C) 106.33
D) 105.00
4) Generally, a bond can be valued as a package of
A) annuity and perpetuity only.
B) perpetuity and single payment only.
C) annuity and single payment only.
D) annuity, perpetuity, and single payment.
A government bond issued in France has a coupon rate of 5 percent, a face value of 100.00 euros, and matures in five years. The bond pays annual interest payments. Calculate the yield to maturity of the bond (in euros) if the price of the bond is 106.00 euros.
A) 5.00%
B) 3.80%
C) 3.66%
D) 6.00%
6) You buy a 12-year 10 percent annual coupon bond at par value, $1,000. You sell the bond three years later for $1,100. What is your rate of return over this three-year period?
A) 40 percent
B) 10 percent
C) 20 percent
D) 30 percent
If a bond pays interest semiannually, then it pays interest
A) once per year.
B) every six months.
C) every three months.
D) every two years.
8) A three-year bond with 10 percent coupon rate and $1,000 face value yields 8 percent. Assuming annual coupon payments, calculate the price of the bond.
A) $857.96
B) $951.96
C) $1,000.00
D) $1,051.54
A five-year treasury bond with a coupon rate of 8 percent has a face value of $1,000. What is the semiannual interest payment?
A) $80
B) $40
C) $100
D) $50
10) A three-year bond has an 8.0 percent coupon rate and a $1,000 face value. If the yield to maturity on the bond is 10 percent, calculate the price of the bond assuming that the bond makes semiannual coupon payments.
A) $857.96
B) $949.24
C) $1,057.54
D) $1,000.00
A four-year bond has an 8 percent coupon rate and a face value of $1,000. If the current price of the bond is $878.31, calculate the yield to maturity of the bond (assuming annual interest payments).
A) 8 percent
B) 10 percent
C) 12 percent
D) 6 percent
12) A five-year bond with a 10 percent coupon rate and $1,000 face value is selling for $1,123. Calculate the yield to maturity on the bond assuming annual interest payments.
A) 10.0 percent
B) 8.9 percent
C) 7.0 percent
D) 5.0 percent
Which of the following statements about the relationship between interest rates and bond prices is true?
A) There is an inverse relationship between bond prices and interest rates, and the price of long-term bonds fluctuates more than the price of short-term bonds for a given change in interest rates (assuming that the coupon rate is the same for both).
B) There is an inverse relationship between bond prices and interest rates, and the price of short-term bonds fluctuates more than the price of long-term bonds for a given change in interest rates (assuming that the coupon rate is the same for both).
C) There is a direct relationship between bond prices and interest rates, and the price of short-term bonds fluctuates more than the price of long-term bonds for a given change in interest rates (assuming that the coupon rate is the same for both).
D) There is a direct relationship between bond prices and interest rates, and the price of long-term bonds fluctuates more than the price of short-term bonds for a given change in interest rates (assuming that the coupon rate is the same for both).
14) Consider a bond with a face value of $1,000, an annual coupon rate of 6 percent, a yield to maturity of 8 percent, and 10 years to maturity. This bond’s duration is
A) 8.7 years.
B) 7.6 years.
C) 10.0 years.
D) 6.5 years.
A bond has a face value of $1,000, an annual coupon rate of 7 percent, yield to maturity of 10 percent, and 20 years to maturity. The bond’s duration is
A) 10.0 years.
B) 7.4 years.
C) 20.0 years.
D) 12.6 years.
16) A bond has a face value of $1,000, a coupon rate of 0 percent, yield to maturity of 9 percent, and 10 years to maturity. This bond’s duration is
A) 6.7 years.
B) 7.5 years.
C) 9.6 years.
D) 10.0 years.
A bond with duration of 10 years has a yield to maturity of 10 percent. This bond’s volatility (modified duration) is
A) 9.09 percent.
B) 6.80 percent.
C) 14.6 percent.
D) 10.00 percent.
18) A bond with duration of 5.7 years has a yield to maturity of 9 percent. The bond’s volatility (modified duration) is
A) 1.9 percent.
B) 5.2 percent.
C) 5.7 percent.
D) 9.0 percent.
If a bond’s volatility is 10.00 percent and the interest rate goes down by 0.75 percent (points), then the price of the bond
A) decreases by 10.00 percent.
B) decreases by 7.50 percent.
C) increases by 7.50 percent.
D) increases by 0.75 percent.
20) If a bond’s volatility is 5.0 percent and its yield to maturity changes by 0.5 percent (points), then the price of the bond
A) changes by 5.0 percent.
B) changes by 2.5 percent.
C) changes by 7.5 percent.
D) will not change.
The volatility of a bond is given by
A) duration/(1 + yield) only.
B) slope of the curve relating the bond price to the interest rate only.
C) yield to maturity only.
D) duration/(1 + yield) and slope of the curve relating the bond price to the interest rate only.
22) One can best describe the term structure of interest rates as the relationship between
A) spot interest rates and bond prices.
B) spot interest rates and stock prices.
C) spot interest rates and time.
D) yields of coupon bonds and their maturity.
The interest rate represented by “r2” is the
A) spot rate on a one-year investment.
B) spot rate on a two-year investment.
C) expected spot rate two years from today.
D) expected spot rate one year from today.
24) If the nominal interest rate per year is 10 percent and the inflation rate is 4 percent, what is the real rate of interest?
A) 10.0 percent
B) 4.1 percent
C) 5.8 percent
D) 14.0 percent
Mr. X invests $1,000 at a 10 percent nominal rate for one year. If the inflation rate is 4 percent, what is the real value of the investment at the end of one year?
A) $1,100
B) $1,000
C) $1,058
D) $1,040
26) Which bond is more sensitive to an interest rate change of 0.75 percent?
Bond A: YTM = 4.00%, maturity = 8 years, coupon = 6% or $60, par value = $1,000.
Bond B: YTM = 3.50%, maturity = 5 years, coupon = 7% or $70, par value = $1,000.
A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Both are equally sensitive.
D) Cannot be determined
As CFO of your corporation, you would prefer (all else equal) to see the price of your corporation’s bonds
A) increase, indicating that bond investors view your firm as less risky.
B) decrease, indicating that bond investors view your firm as less risky.
C) increase, indicating that bond investors view your firm as more willing to take risks.
D) decrease, indicating that bond investors view your firm as more willing to take risks.
28) Which of the following bonds has the longest duration?
A) 5-year coupon bond
B) 5-year, zero-coupon bond
C) 10-year coupon bond
D) 10-year, zero-coupon bond
29) Which of the following bonds has the greatest volatility?
A) 5-year coupon bond
B) 5-year, zero-coupon bond
C) 10-year coupon bond
D) 10-year, zero-coupon bond
1) The major secondary market for Boeing shares is:
A) London Stock Exchange.
B) New York Stock Exchange.
C) Hang Seng.
D) Tokyo Stock Exchange.
2) Assume Boeing has about 10.3 billion shares outstanding and the stock price is $37.10. Also, assume the P/E ratio is about 18.3. Calculate the approximate market capitalization for GE.
A) $679 billion
B) $188 billion
C) $382 billion
D) $103 billion
The following are foreign companies that are traded on the New York Stock Exchange:
A) Sony, Telefonica Brasil, and Canadian Pacific only.
B) Sony, Telefonica Brasil, Canadian Pacific, Deutsche Bank, China Eastern Airlines, and Tata Motors.
C) Sony, Telefonica Brasil, Canadian Pacific, and General Electric only.
D) all of the given companies.
4) The dividend yield reported on finance.yahoo.com is calculated as follows:
A) (dividend/year-high stock price).
B) (dividend/year-low stock price).
C) (dividend/closing stock price).
D) (dividends/earnings).
A Wall Street Journal quotation for a company has the following values: Div: $1.12, PE: 18.3, Close: $37.22. Calculate the approximate dividend payout ratio for the company.
A) 18 percent
B) 35 percent
C) 45 percent
D) 55 percent
6) If a Wall Street Journal quotation for a company has the values Close = 55.14 and Net change = +1.04, then what was the closing price for the stock for the previous trading day?
A) $56.18
B) $54.10
C) $55.66
D) $53.02
The following are auction markets EXCEPT:
A) New York Stock Exchange.
B) London Stock Exchange.
C) Tokyo Stock Exchange.
D) Nasdaq.
8) The following is an example of a dealer market:
A) New York Stock Exchange
B) London Stock Exchange
C) Tokyo Stock Exchange
D) Nasdaq
9) In which of the following exchanges does a computer act as the sole auctioneer?
A) New York Stock Exchange, London Stock Exchange, Tokyo Stock Exchange, and Deutsche Borse
B) New York Stock Exchange, Tokyo Stock Exchange, and Deutsche Borse only
C) New York Stock Exchange, London Stock Exchange, and Tokyo Stock Exchange only
D) London Stock Exchange, Shanghai Stock Exchange, Tokyo Stock Exchange, and Deutsche Borse only
Super Computer Company’s stock is selling for $100 per share today. It is expected that–at the end of one year–it will pay a dividend of $6 per share and then be sold for $114 per share. Calculate the expected rate of return for the shareholders.
A) 20 percent
B) 15 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 25 percent
11) The valuation of a common stock today primarily depends on
A) the number of shares outstanding and the number of its shareholders.
B) its expected future dividends and its discount rate.
C) Wall Street analysts.
D) the price to earnings ratio.
12) CK Company stockholders expect to receive a year-end dividend of $5 per share and then immediately sell their shares for $115 dollars per share. If the required rate of return for the stock is 20 percent, what is the current value of the stock?
A) $132
B) $122
C) $100
D) $110
Deluxe Company expects to pay a dividend of $2 per share at the end of year 1, $3 per share at the end of year 2, and then be sold for $32 per share at the end of year 2. If the required rate of return on the stock is 15 percent, what is the current value of the stock?
A) $28.20
B) $32.17
C) $32.00
D) $29.18
14) Casino Inc. expects to pay a dividend of $3 per share at the end of year 1 (Div1) and these dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 6 percent per year forever. If the required rate of return on the stock is 18 percent, what is the current value of the stock today?
A) $25
B) $50
C) $100
D) $54
The constant dividend growth formula P0 = Div1/(r – g) assumes
A) that dividends grow at a constant rate g, forever only.
B) r > g only.
C) that dividends grow at a constant rate g, forever, and r > g only.
D) g is never negative only.
16) Will Co. is expected to pay a dividend of $2 per share at the end of year 1(Div1), and the dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4 percent forever. If the current price of the stock is $20 per share, calculate the expected return or the cost of equity capital for the firm.
A) 10 percent
B) 4 percent
C) 14 percent
D) 20 percent
World-Tour Co. has just now paid a dividend of $2.83 per share (Div0); its dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 6 percent per year forever. If the required rate of return on the stock is 16 percent, what is the current value of the stock, after paying the dividend?
A) $70
B) $56
C) $30
D) $48
18) One can estimate the expected rate of return or the cost of equity capital as follows:
A) Dividend yield – expected rate of growth in dividends.
B) Dividend yield + expected rate of growth in dividends.
C) Dividend yield/expected rate of growth in dividends.
D) (Dividend yield) × (expected rate of growth in dividends).
19) One can estimate the dividend growth rate for a stable firm as
A) plow-back rate/the return on equity (ROE).
B) plow-back rate – the return on equity (ROE).
C) plow-back rate + the return on equity (ROE).
D) plow-back rate × the return on equity (ROE).
MJ Co. pays out 60 percent of its earnings as dividends. Its return on equity is 15 percent. What is the stable dividend growth rate for the firm?
A) 9 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 6 percent
D) 15 percent
21) Michigan Co. just paid a dividend of $2 per share. Analysts expect future dividends to grow at 20 percent per year for the next four years and then grow at 6 percent per year thereafter. Calculate the expected dividend in year 5.
A) $4.15
B) $2.95
C) $4.40
D) $3.81
22) Otobai Motor Company just paid a dividend of $1.40. Analysts expect its dividend to grow at a rate of 18 percent for the next three years and then a constant rate of 5 percent thereafter. What is the expected dividend per share at the end of year 5?
A) $2.35
B) $2.54
C) $2.91
D) $1.50
The In-Tech Co. just paid a dividend of $1 per share. Analysts expect its dividend to grow at 25 percent per year for the next three years and then 5 percent per year thereafter. If the required rate of return on the stock is 18 percent, what is the current value of the stock?
A) $12.97
B) $11.93
C) $15.20
D) $15.78
24) R&D Technology Corporation just paid a dividend of $0.50 per share. Analysts expect its dividend to grow at 24 percent per year for the next two years and then 8 percent per year thereafter. If the required rate of return in the stock is 16 percent, calculate the current value of the stock.
A) $1.11
B) $7.71
C) $8.82
D) $10.38
Ocean Co. just paid a dividend of $2 per share out of earnings of $4 per share. If the book value per share is $25, what is the expected growth rate in dividends (g)?
A) 16 percent
B) 12 percent
C) 8 percent
D) 4 percent
26) Seven-Seas Co. just paid a dividend of $3 per share out of earnings of $5 per share. If its book value per share is $40.00 and its market price is $52.50 per share, calculate the required rate of return on the stock.
A) 12 percent
B) 11 percent
C) 5 percent
D) 6 percent
River Co. just paid a dividend of $2 per share out of earnings of $4 per share. If its book value per share is $25 and its stock is currently selling for $40 per share, calculate the required rate of return on the stock.
A) 15.2 percent
B) 7.2 percent
C) 14.7 percent
D) 13.4 percent
28) Lake Co. just paid a dividend of $3 per share out of earnings of $5 per share. If its book value per share is $40, what is the expected growth rate in dividends?
A) 7.5 percent
B) 8 percent
C) 12.5 percent
D) 5 percent
The growth rate in dividends is a function of two ratios. They are
A) ROA and ROE.
B) dividend yield and growth rate in stock price.
C) ROE and the plowback ratio.
D) book value per share and EPS.
30) Company X has a P/E ratio of 10 and a stock price of $50 per share. Calculate earnings per share of the company.
A) $6 per share
B) $10 per share
C) $0.20 per share
D) $5 per share

更多代写:阿德莱德留学生CS网课代修 pte代考 英国Accounting代考价格 加拿大论文代写 文书代写 留学微积分网课代修
合作平台:essay代写 论文代写 写手招聘 英国留学生代写
I218 Computer ArchitectureReport 3 计算机体系结构cs代写 (1) In the textbook and lecture slides, detailed information in the pipeline registers (IF/ID, ID/EX, EX/MEM, MEM/WB) is not provided. ...
View detailsI218 Computer ArchitectureReport 2 cs计算机体系结构作业代做 (1)How is the instruction “sub $t9, $s4, $s7” translated to a machine instruction code? Answer the rs, rt, and rd fields in binary n...
View detailsEconomics 426: Problem Set 1 – Robinson Crusoe 经济问题集代做 I. Robin Crusoe is endowed with 112 labor-hours per week. There is a production function for the output of oysters Spring...
View detailsEconomics 426: Problem Set 8 – Production 经济学生产问题代写 I. Show that if A and B are closed subsets of Rn , then A+B is closed or provide a counter example. (20 pts) II. Show that if A and...
View details