金融市场经济学代写 C-CAPM代写 ECONOMICS代写
1081ECONOMICS OF FINANCIAL MARKETS 金融市场经济学代写 For the representative agent consumption-based capital asset pricing model (C-CAPM), the price of a financial asset is affected ____ by _____: ...
View detailsSearch the whole station
经济考试助攻 Ch 1 WHY STUDY MONEY, BANKING, AND FINANCIAL MARKETS? 1. Financial markets promote economic efficiency by ________.
1. Financial markets promote economic efficiency by ________.
A) channelling funds from investors to savers
B) creating inflation
C) channelling funds to those who have a productive use for them
D) reducing investment
2. Markets in which funds are transferred from those who do not have a productive use for them to those who do are called ________.
A) commodity markets
B) fund-available markets
C) derivative exchange markets
D) financial markets
3. A security is also known as ________.
A) a financial instrument
B) a contingent claim
C) the interest rate
D) a liability
4. The interest rate on long-term corporate bonds is ________, on average, than other interest rates. The spread between it an other rates ________ over time.
A) lower; remains constant
B) lower; fluctuates
C) higher; remains constant
D) higher; fluctuates
5. An increase in interest rates might ________ saving because more can be earned in interest income.
A) encourage
B) discourage
C) disallow
D) invalidate
6. Everything else held constant, an increase in interest rates on student loans ________.
A) may increase the cost of education
B) may reduce the cost of education
C) has no effect on educational costs
D) increases costs for students with no loans
7. A share of common stock is a claim on a corporation’s ________.
A) debt
B) liabilities
C) expenses
D) earnings and assets
8. Lower interest rates might cause a corporation to ________ building a new plant that would provide more jobs.
A) complete
B) postpone
C) consider
D) start
9. The stock market is important because it is ________.
A) where interest rates are determined
B) the most widely followed financial market in the Canada
C) where foreign exchange rates are determined
D) the market where most borrowers get their funds
10. Changes in stock prices ________.
A) do not affect people’s wealth and their willingness to spend
B) affect firms’ decisions to sell stock to finance investment spending
C) are predictable
D) are unimportant to decision makers
11. The bond markets are important because they are ________.
A) easily the most widely followed financial markets in Canada
B) the markets where foreign exchange rates are determined
C) where corporations and governments borrow to finance their activities
D) the markets where all borrowers get their funds
12. Financial crises are characterized by ________.
A) surging employment
B) hyperinflation
C) decline in asset prices
D) high profits in the financial sector
13. Chartered banks, trust and mortgage loan companies, and credit unions and caisses populaires ________.
A) no longer provide financial intermediation
B) since deregulation now provide services only to small depositors
C) accept deposits and make loans
D) create fluctuations in the stock market
14. Which of the following are the largest financial intermediaries in the Canadian economy?
A) Insurance companies
B) Finance companies
C) Banks
D) Mutual funds
15. Evidence from business cycle fluctuations in Canada indicates that ________.
A) a negative relationship between money growth and general economic activity exists
B) recessions have been preceded by declines in share prices on the stock exchange
C) recessions have been preceded by dollar depreciation
D) recessions have been preceded by a decline in the growth rate of money
16. ________ theory relates changes in the quantity of money to changes in aggregate economic activity and the price level.
A) Monetary
B) Fiscal
C) Financial
D) Systemic
17. A sharp increase in the growth of the money supply is likely followed by ________.
A) a recession
B) a depression
C) an increase in the inflation rate
D) no change in the economy
18. Which of the following is a true statement?
A) Money or the money supply is defined as Bank of Canada notes.
B) The average price of goods and services in an economy is called the aggregate price level.
C) The inflation rate is measured as the rate of change in the federal government budget deficit.
D) The aggregate price level is measured as the rate of change in the inflation rate.
19. There is a ________ association between inflation and the growth rate of money ________.
A) positive; demand
B) positive; supply
C) negative; demand
D) negative; supply
20. A budget ________ occurs when government expenditures exceed tax revenues for a particular time period.
A) deficit
B) surplus
C) surge
D) surfeit
21. Budget deficits are important because deficits ________.
A) cause bank failures
B) always cause interest rates to fall
C) may lead to a financial crisis
D) always cause prices to fall
22. Canadian companies can borrow funds ________.
A) only in Canadian financial markets
B) only in foreign financial marketsC) in both Canadian and foreign financial markets
D) only from the Canadian government
23. The price of one country’s currency in terms of another country’s currency is called the ________.
A) foreign exchange rate
B) interest rate
C) TSE index
D) inflation rate
24. The foreign exchange rate is ________.
A) determined by the banks
B) not important to Canadian individuals
C) the relative price of two currencies
D) the ratio of the foreign aggregate price level to the domestic aggregate price level
25. Everything else constant, a stronger Canadian dollar will mean that ________.
A) vacationing in England becomes more expensive
B) vacationing in England becomes less expensive
C) French cheese becomes more expensive
D) Japanese cars become more expensive
26. Budget deficits can be a concern because they might ________.
A) ultimately lead to higher inflation
B) lead to lower interest rates
C) lead to a slower rate of money growth
D) lead to higher bond prices
27. Financial markets have the basic function of ________.
A) getting people with funds to lend together with people who want to borrow funds
B) assuring that the swings in the business cycle are less pronounced
C) assuring that governments need never resort to printing money
D) providing a risk-free repository of spending power
28. Financial markets improve economic welfare because ________.
A) they channel funds from investors to savers
B) they allow consumers to time their purchase better
C) they weed out inefficient firms
D) eliminate the need for indirect finance
29. A breakdown of financial markets can result in ________.
A) financial stability
B) rapid economic growth
C) political instability
D) stable prices
30. Which of the following can be described as direct finance?
A) You take out a mortgage from your local bank.
B) You borrow $2500 from a friend.
C) You buy shares of common stock in the secondary market.
D) You buy shares in a mutual fund.
31. Which of the following can be described as involving direct finance?
A) A corporation takes out loans from a bank.
B) People buy shares in a mutual fund.
C) A corporation buys a short-term corporate security in a secondary market.
D) People buy shares of common stock in the primary markets.
32. Which of the following can be described as involving indirect finance?
A) You make a loan to your neighbor.
B) A corporation buys a share of common stock issued by another corporation in the primary market.
C) You buy a Canadian Treasury bill from the Bank of Canada.
D) You make a deposit at a bank.
33. Securities are ________ for the person who buys them, but are ________ for the individual or firm that issues them.
A) assets; liabilities
B) liabilities; assets
C) negotiable; nonnegotiable
D) nonnegotiable; negotiable
34. When I purchase a corporate ________, I am lending the corporation funds for a specific time. When I purchase a corporation’s ________, I become an owner in the corporation.
A) bond; stock
B) stock; bond
C) stock; debt security
D) bond; debt security
35. Which of the following statements about the characteristics of debt and equities is true?
A) They can both be long-term financial instruments.
B) Bond holders are residual claimants.
C) The income from bonds is typically more variable than that from equities.
D) Bonds pay dividends.
36. Which of the following statements about financial markets and securities is true?
A) A bond is a long-term security that promises to make periodic payments called dividends to the firm’s residual claimants.
B) A debt instrument is intermediate term if its maturity is less than one year.
C) A debt instrument is intermediate term if its maturity is ten years or longer.
D) The maturity of a debt instrument is the number of years (term) to that instrument’s expiration date.
37.Which of the following is an example of an intermediate-term debt?
A) A thirty-year mortgage
B) A sixty-month car loan
C) A six month loan from a finance company
D) A Treasury bond
38.Long-term debt has a maturity that is ________.
A) between one and ten years
B) less than a year
C) between five and ten years
D) ten years or longer
39.Which of the following benefit directly from any increase in the corporation’s profitability?
A) A bond holder
B) A commercial paper holder
C) A shareholder
D) A T-bill holder
40.A financial market in which previously issued securities can be resold is called a ________ market.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) used securities
41.________ work in the secondary markets matching buyers with sellers of securities.
A) Dealers
B) Underwriters
C) Brokers
D) Claimants
42.An important function of secondary markets is to ________.
A) make it easier to sell financial instruments to raise funds
B) raise funds for corporations through the sale of securities
C) make it easier for governments to raise taxes
D) create a market for newly constructed houses
43.Secondary markets make financial instruments more ________.
A) solid
B) vapid
C) liquid
D) risky
44.A liquid asset is ________.
A) an asset that can easily and quickly be sold to raise cash
B) a share of an ocean resort
C) difficult to resell
D) always sold in an over-the-counter market
45.Treasury bills pay no interest but are sold at a ________. That is, you will pay a lower purchase price than the amount you receive at maturity.
A) premium
B) collateral
C) default
D) discount
46.Treasury bills are considered the safest of all money market instruments because there is no risk of ________.
A) defeat
B) default
C) desertion
D) demarcation
47.A debt instrument sold by a bank to its depositors that pays annual interest of a given amount and at maturity pays back the original purchase price is called ________.
A) commercial paper
B) a negotiable certificate of deposit
C) a municipal bond
D) federal funds
48.A short-term debt instrument issued by well-known corporations is called ________.
A) commercial paper
B) corporate bonds
C) municipal bonds
D) commercial mortgages
49.Collateral is ________ the lender receives if the borrower does not pay back the loan.
A) a liability
B) an asset
C) a present
D) an offering
50. You can borrow $5000 to finance a new business venture. This new venture will generate annual earnings of $251. The maximum interest rate that you would pay on the borrowed funds and still increase your income is ________.
A) 25 percent
B) 12.5 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 5 percent
51.Which of the following instruments are traded in a money market?
A) Provincial government bonds
B) Treasury bills
C) Corporate bonds
D) Government agency securities
52.Bonds issued by corporations are called ________ bonds.
A) corporate
B) Treasury
C) municipal
D) commercial
53.Equity and debt instruments with maturities greater than one year are called ________ market instruments.
A) capital
B) money
C) federal
D) benchmark
54.One reason for the extraordinary growth of foreign financial markets is ________.
A) decreased trade
B) increases in the pool of savings in foreign countries
C) the recent introduction of the foreign bond
D) slower technological innovation in foreign markets
55.Bonds that are sold in a foreign country and are denominated in the country’s currency in which they are sold are known as ________.
A) foreign bonds
B) Eurobonds
C) equity bonds
D) country bonds
56. When an investment bank ________ securities, it guarantees a price for a corporation’s securities and then sells them to the public.
A) underwrites
B) undertakes
C) overwrites
D) overtakes
57.The time and money spent in carrying out financial transactions are called ________.
A) economies of scale
B) financial intermediation
C) liquidity services
D) transaction costs
58.Financial intermediaries provide customers with liquidity services. Liquidity services ________.
A) make it easier for customers to conduct transactions
B) allow customers to have a cup of coffee while waiting in the lobby
C) are a result of the asymmetric information problem
D) are another term for asset transformation
59.The process where financial intermediaries create and sell low-risk assets and use the proceeds to purchase riskier assets is known as ________.
A) risk sharing
B) risk aversion
C) risk neutrality
D) risk selling
60. Reducing risk through the purchase of assets whose returns do not always move together is ________.
A) diversification
B) intermediation
C) intervention
D) discounting
61. The concept of diversification is captured by the statement ________.
A) don’t look a gift horse in the mouth
B) don’t put all your eggs in one basket
C) it never rains, but it pours
D) make hay while the sun shines
62. Typically, borrowers have superior information relative to lenders about the potential returns and risks associated with an investment project. The difference in information is called ________.
A) moral selection
B) risk sharing
C) asymmetric information
D) adverse hazard
63.Adverse selection is a problem associated with equity and debt contracts arising from ________.
A) the lender’s relative lack of information about the borrower’s potential returns and risks of his investment activities
B) the lender’s inability to legally require sufficient collateral to cover a 100 percent loss if the borrower defaults
C) the borrower’s lack of incentive to seek a loan for highly risky investments
D) the borrower’s lack of good options for obtaining funds
64. If bad credit risks are the ones who most actively seek loans and, therefore, receive them from financial intermediaries, then financial intermediaries face the problem of ________.
A) moral hazard
B) adverse selection
C) free-riding
D) costly state verification
65.The primary liabilities of a chartered bank are ________.
A) bonds
B) mortgages
C) deposits
D) commercial paper
66. Contractual savings institutions include ________.
A) mutual savings banks
B) money market mutual funds
C) commercial banks
D) life insurance companies
67.An investment intermediary that lends funds to consumers is ________.
A) a finance company
B) an investment bank
C) a finance fund
D) a consumer company
68.________ are financial intermediaries that acquire funds by selling shares to many individuals and using the proceeds to purchase diversified portfolios of stocks and bonds.
A) Mutual funds
B) Investment banks
C) Finance companies
D) Credit unions
69.An important feature of money market mutual fund shares is ________.
A) deposit insurance
B) they offer deposit-type accounts
C) the ability to borrow against shareholdings
D) claims on shares of corporate stock
70.The Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation regulates ________.
A) brokerage firms
B) banks
C) credit unions
D) mutual funds
71. A person’s house is part of her ________.
A) money
B) income
C) liabilities
D) wealth
72.Money is ________.
A) anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods and services or in the repayment of debt
B) a flow of earnings per unit of time
C) the total collection of pieces of property that are a store of value
D) always based on a precious metal like gold or silver
73. Currency includes ________.
A) paper money and coins
B) paper money, coins, and cheques
C) paper money and cheques
D) paper money, coins, cheques, and savings deposits
74.Even economists have no single, precise definition of money because ________.
A) money supply statistics are a state secret
B) the Bank of Canada does not employ or report different measures of the money supply
C) the “moneyness” or liquidity of an asset is a matter of degree
D) economists find disagreement interesting and refuse to agree for ideological reasons
75.When we say that money is a stock variable, we mean that ________.
A) the quantity of money is measured at a given point in time
B) we must attach a time period to the measure
C) it is sold in the equity market
D) money never loses purchasing power
76.Which of the following is a true statement?
A) Money and income are flow variables.
B) Money is a flow variable.
C) Income is a flow variable.
D) Money and income are stock variables.
77.If peanuts serve as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value, then
peanuts are ________.
A) bank deposits
B) reserves
C) money
D) loanable funds
78.Compared to an economy that uses a medium of exchange, in a barter economy ________.
A) transaction costs are higher
B) transaction costs are lower
C) liquidity costs are higher
D) liquidity costs are lower
79.Of money’s three functions, the one that distinguishes money from other assets is its function as a ________.
A) store of value
B) unit of account
C) standard of deferred payment
D) medium of exchange
80. ________ is used to make purchases while ________ is the total collection of pieces of property that serve to store value.
A) Money; income
B) Wealth; income
C) Income; money
D) Money; wealth
81.The conversion of a barter economy to one that uses money ________.
A) increases efficiency by reducing the need to exchange goods and services
B) increases efficiency by reducing the need to specialize
C) increases efficiency by reducing transactions costs
D) does not increase economic efficiency
82.Which of the following statements best explains how the use of money in an economy increases economic efficiency?
A) Money increases economic efficiency because it is costless to produce.
B) Money increases economic efficiency because it discourages specialization.
C) Money increases economic efficiency because it decreases transactions costs.
D) Money cannot have an effect on economic efficiency.
83. Which of the following is a true statement?
A) The conversion of a barter economy to one that uses money increases efficiency by increasing the cost of exchange.
B) The conversion of a barter economy to one that uses money increases efficiency by increasing the cost to those who wish to specialize.
C) The conversion of a barter economy to one that uses money increases efficiency by reducing transactions costs.
D) The conversion of a barter economy to one that uses money does not increases efficiency.
84.Whatever a society uses as money, the distinguishing characteristic is that it must ________.
A) be completely inflation proof
B) be generally acceptable as payment for goods and services or in the repayment of debt
C) contain gold
D) be produced by the government
85.Because it is a unit of account, money ________.
A) increases transaction costs
B) reduces the number of prices that need to be calculated
C) does not earn interest
D) discourages specialization
86. ________ is the relative ease and speed with which an asset can be converted into a medium of exchange.
A) Efficiency
B) Liquidity
C) Deflation
D) Specialization
87. Monetary aggregates are ________.
A) measures of the money supply reported by the Bank of Canada
B) measures of the wealth of individuals
C) never redefined since “money” never changes
D) reported by the Department of Finance annually
88. A fall in the level of prices ________.
A) does not affect the value of money
B) has an uncertain effect on the value of money
C) increases the value of money
D) reduces the value of money
89. During hyperinflations, ________.
A) the value of money rises rapidly
B) money no longer functions as a good store of value and people may resort to barter transactions on a much larger scale
C) middle-class savers benefit as prices rise
D) money’s value remains fixed to the price level; that is, if prices double so does the value of money
90. A disadvantage of ________ is that it can be very heavy and hard to transport from one place to another.
A) commodity money
B) fiat money
C) electronic money
D) paper money
91.The evolution of the payments system from barter to precious metals, then to fiat money, then to cheques can best be understood as a consequence of the fact that ________.
A) paper is more costly to produce than precious metals
B) precious metals were not generally acceptable
C) precious metals were difficult to carry and transport
D) paper money is less accepted than cheques
92.Introduction of cheques into the payments system reduced the costs of exchanging goods and services. Another advantage of cheques is that ________.
A) they provide convenient receipts for purchases
B) they can never be stolen
C) they are more widely accepted than currency
D) the funds from a deposited cheque are available for use immediately
93.The evolution of the payments system from barter to precious metals, then to fiat money, then to cheques can best be understood as a consequence of ________.
A) government regulations designed to improve the efficiency of the payments system
B) government regulations designed to promote the safety of the payments system
C) innovations that reduced the costs of exchanging goods and services
D) competition among firms to make it easier for customers to purchase their products
94.Compared to an electronic payments system, a payments system based on cheques has the major drawback that ________.
A) cheques are less costly to process
B) cheques take longer to process, meaning that it may take several days before the depositor can get her cash
C) fraud may be more difficult to commit when paper receipts are eliminated
D) legal liability is more clearly defined
95.Which of the following sequences accurately describes the evolution of the payments system?
A) Barter, coins made of precious metals, paper currency, cheques, electronic funds transfers
B) Barter, coins made of precious metals, cheques, paper currency, electronic funds transfers
C) Barter, cheques, paper currency, coins made of precious metals, electronic funds transfers
D) Barter, cheques, paper currency, electronic funds transfers
96.Which of the following is not a form of e-money?
A) A debit card
B) A credit card
C) A stored-value card
D) A smart card
97.If an individual moves money from a demand deposit account to a money market mutual fund, ________.
A) M1+ decreases and M2 stays the same
B) M1+ stays the same and M2+ increases
C) M1+ stays the same and M2 stays the same
D) M1+ decreases and M2 decreases
98.If an individual moves money from a chequing account to a money market mutual fund, ________.
A) M1+ decreases and M2+ increases
B) M1+ stays the same and M2+ increases
C) M1+ decreases and M2+ stays the same
D) M1+ increases and M2+ decreases
99.The currency component includes paper money and coins held in ________.
A) bank vaults
B) ATMs
C) the hands of the nonbank public
D) the central bank
100. The M1+ measure of money includes ________.
A) small denomination time deposits
B) chequable deposits
C) money market deposit accounts
D) money market mutual fund shares
101. Which of the following is not included in the measure of M2?
A) Personal deposits
B) Non-personal demand deposits
C) Currency
D) Foreign currency deposits
102. Which of the following is included in both M1+ and M2?
A) Currency
B) Savings deposits
C) Small-denomination time deposits
D) Money market deposit accounts
103. If an individual moves money from a notice deposit at a bank to a deposit account at a credit union, ________.
A) M2 decreases and M2+ stays the same
B) M2 decreases and M2+ increases
C) M2 increases and M2+ stays the same
D) M2 increases and M2+ increases
104. A hyperinflation is ________.
A) a period of extreme inflation generally greater than 50 percent per month
B) a period of anxiety caused by rising prices
C) an increase in output caused by higher prices
D) impossible today because of tighter regulations
105.The measures of money supply used by the Bank of Canada are ________ indices.
A) simple-sum
B) complex
C) multiplicative
D) accurate
106. In the money index used by the Bank of Canada: M = X1 + X2 + … + Xn, the n monetary components have ________.
A) a weight of 1/n
B) different weights
C) a weight of n
D) a weight of 1
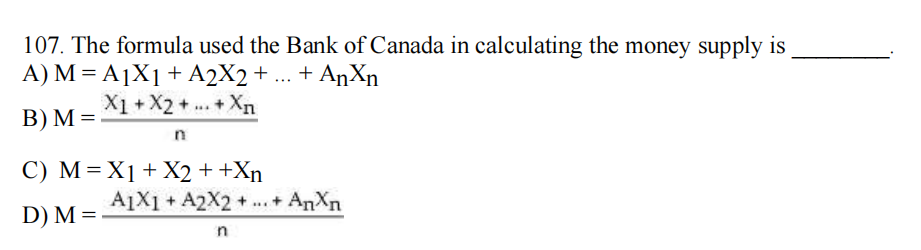
108. The concept of ________ is based on the common-sense notion that a dollar paid to you in the future is less valuable to you than a dollar today.
A) present value
B) future value
C) interest
D) deflation
109. The present value of an expected future payment ________ as the interest rate increases.
A) falls
B) rises
C) is constant
D) is unaffected
110. With an interest rate of 6 percent, the present value of $100 next year is approximately ________.
A) $106
B) $100
C) $94
D) $92
111. A credit market instrument that provides the borrower with an amount of funds that must be repaid at the maturity date along with an interest payment is known as a ________.
A) simple loan
B) fixed-payment loan
C) coupon bond
D) discount bond
112. The concept of ________ is based on the common-sense notion that a dollar paid to you in the future is less valuable to you than a dollar today.
A) present value
B) future value
C) interest
D) deflation
113. Which of the following is true of fixed payment loans?
A) The borrower repays both the principal and interest at the maturity date.
B) Installment loans and mortgages are frequently of the fixed payment type.
C) The borrower pays interest periodically and the principal at the maturity date.
D) Commercial loans to businesses are often of this type.
114. A credit market instrument that pays the owner a fixed coupon payment every year until the maturity date and then repays the face value is called a ________.
A) simple loan
B) fixed-payment loan
C) coupon bond
D) discount bond
115. When talking about a coupon bond, face value and ________ mean the same thing.
A) par value
B) coupon value
C) amortized value
D) discount value
116. The dollar amount of the yearly coupon payment expressed as a percentage of the face value of the bond is called the bond’s ________.
A) coupon rate
B) maturity rate
C) face value rate
D) payment rate
117. If a $5000 coupon bond has a coupon rate of 13 percent, then the coupon payment every year is ________.
A) $650
B) $1300
C) $130
D) $13
118. The price of a perpetuity that has a coupon of $50 per year and a yield to maturity of 2.5% is
A) 1800
B) 1900
C) 2000
D) 2100
119. The interest rate that equates the present value of payments received from a debt instrument with its value today is the ________.
A) simple interest rate
B) current yield
C) yield to maturity
D) real interest rate
120. The yield to maturity on a $1,000-face-value discount bond maturing in one year that sells for $800 is:
A) 20%
B) 25%
C) 28%
D) 15%
121. If $22050 is the amount payable in two years for a $20000 simple loan made today, the interest rate is ________.
A) 5 percent
B) 10 percent
C) 22 percent
D) 25 percent
122. If a security pays $110 next year and $121 the year after that, what is its yield to maturity if it sells for $200?
A) 9 percent
B) 10 percent
C) 11 percent
D) 12 percent
123. Which of the following is true for a coupon bond?
A) When the coupon bond is priced at its face value, the yield to maturity equals the coupon rate.
B) The price of a coupon bond and the yield to maturity are positively related.
C) The yield to maturity is greater than the coupon rate when the bond price is above the par value.
D) The yield is less than the coupon rate when the bond price is below the par value.
124. If a perpetuity has a price of $500 and an annual interest payment of $25, the interest rate is ________.
A) 2.5 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 7.5 percent
D) 10 percent
125. A coupon bond that has no maturity date and no repayment of principal is called a ________.
A) consol
B) cabinet
C) Treasury bill
D) Government note
126. If a perpetuity has a price of $500 and an annual interest payment of $25, the interest rate is ________.
A) 2.5 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 7.5 percent
D) 10 percent
127. The yield to maturity for a one-year discount bond equals the increase in price over the year, divided by the ________.
A) initial price
B) face value
C) interest rate
D) coupon rate
128. If a $5000 face-value discount bond maturing in one year is selling for $5000, then its yield to maturity is ________.
A) 0 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 20 percent
129. Which of the following is true concerning the distinction between interest rates and returns?
A) The rate of return on a bond will not necessarily equal the interest rate on that bond.
B) The return can be expressed as the difference between the current yield and the rate of capital gains.
C) The rate of return will be greater than the interest rate when the price of the bond falls between time t and time t + 1.
D) The return can be expressed as the sum of the discount yield and the rate of capital gains.
130. If the interest rates on all bonds rise from 5 to 6 percent over the course of the year, which bond would you prefer to have been holding?
A) A bond with one year to maturity
B) A bond with five years to maturity
C) A bond with ten years to maturity
D) A bond with twenty years to maturity
131. An equal decrease in all bond interest rates ________.
A) increases the price of a five-year bond more than the price of a ten-year bond
B) increases the price of a ten-year bond more than the price of a five-year bond
C) decreases the price of a five-year bond more than the price of a ten-year bond
D) decreases the price of a ten-year bond more than the price of a five-year bond
132. Which of the following $5000 face-value securities has the highest yield-to maturity?
A) A 6 percent coupon bond selling for $5000
B) A 6 percent coupon bond selling for $5500
C) A 10 percent coupon bond selling for $5000
D) A 12 percent coupon bond selling for $4500
133. The riskiness of an asset’s returns due to changes in interest rates is ________.
A) exchange-rate risk
B) price risk
C) asset risk
D) interest-rate risk
134. Bonds whose term-to-maturity is longer than the holding period are subject to ________.
A) interest rate risk
B) exchange-rate risk
C) inflation
D) deflation
135. The nominal interest rate minus the expected rate of inflation ________.
A) defines the real rate of inflation
B) is a worse measure of the incentives to borrow and lend than is the nominal interest rate
C) is a more accurate indicator of the tightness of credit market conditions than is the nominal interest rate
D) defines the bank rate
136. In which of the following situations would you prefer to be the lender?
A) The interest rate is 9 percent and the expected inflation rate is 7 percent.
B) The interest rate is 4 percent and the expected inflation rate is 1 percent.
C) The interest rate is 13 percent and the expected inflation rate is 15 percent.
D) The interest rate is 25 percent and the expected inflation rate is 50 percent.
137. If you expect the inflation rate to be 4 percent next year and a one year bond has a yield to maturity of 7 percent, then the real interest rate on this bond is ________.
A) -3 percent
B) -2 percent
C) 3 percent
D) 7 percent
138. If the interest rates on all bonds rise from 5 to 6 percent over the course of the year, which bond would you prefer to have been holding?
A) A bond with one year to maturity
B) A bond with five years to maturity
C) A bond with ten years to maturity
D) A bond with twenty years to maturity

经济考试助攻
更多代写:Java美国Assignment代写推荐 GMAT代考 英国经济学网课托管价格 美国essay润色 考古学论文代写 代写Essay作业
合作平台:essay代写 论文代写 写手招聘 英国留学生代写
ECONOMICS OF FINANCIAL MARKETS 金融市场经济学代写 For the representative agent consumption-based capital asset pricing model (C-CAPM), the price of a financial asset is affected ____ by _____: ...
View detailsECOM137 China and Global Financial Markets Duration:3hours 金融市场考试代写 Section 1 Are the following statements true or false? If false, give reasons. 1) Money has three main functions: ...
View detailsEC201 Problem Set 4: Price changes and Welfare 价格变化和福利代写 Consumer Price Index (CPI) Discussion The Covid-19 pandemic changed consumer spending as some goods and services were unavailab...
View detailsECON 701 MODULE 7 EXERCISES 微观经济练习代写 Exercise 1 (The Monty Hall Game). The example we now discuss is now fairly well known. The name comes from an American television game show, Ex...
View details